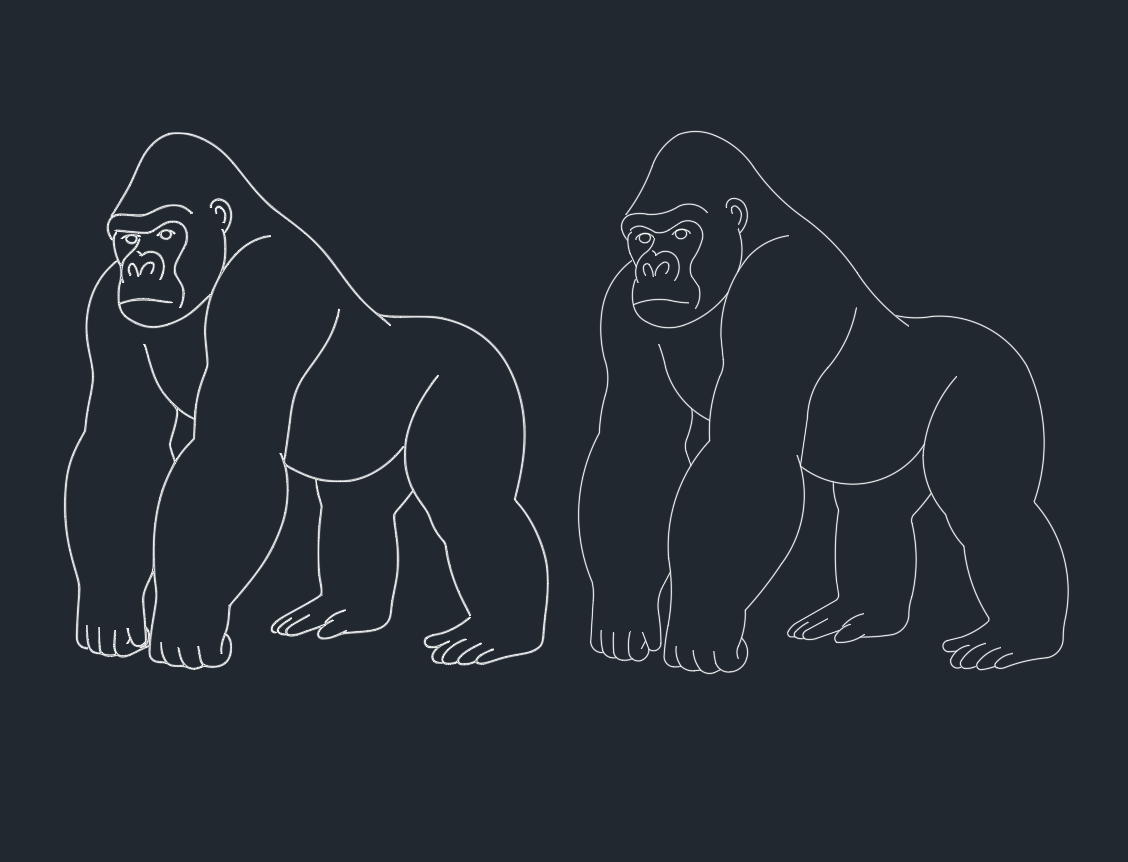
Introduction to Gorillas: Importance in Engineering and CAD Design
Gorillas, the largest living primates, hold significant interest not only in biological studies but also in the fields of engineering, architecture, and CAD design. Their robust anatomy, complex movement patterns, and unique biomechanical features offer valuable insights for professionals designing structural and mechanical systems. Understanding gorilla morphology can inspire innovative solutions in projects requiring strength, stability, and adaptability.
Anatomical Features of Gorillas Relevant to CAD Designers
Gorillas are renowned for their muscular build and skeletal robustness. Their anatomy includes:
– Large, Barrel-Shaped Chest: Supports powerful upper body muscles.
– Long, Strong Arms: Adapted for knuckle-walking and climbing, providing insight into joint articulation and load distribution.
– Dense Bones: Offer models for structural reinforcement in design.
– Opposable Thumbs and Dexterous Fingers: Useful reference for ergonomic design in tools, robotics, and prosthetics.
Engineers and CAD designers can study gorilla bone structure to develop components that require high strength-to-weight ratios, especially in fields like robotics and prosthetics.
Biomechanics of Gorillas: Applications in Engineering
Gorilla biomechanics have direct applications in engineering disciplines. Their skeletal and muscular systems demonstrate how to manage large loads and dynamic forces efficiently. For instance:
– Joint Mechanics: The ball-and-socket shoulder joints of gorillas provide guidance for designing robotic arms with wide ranges of motion.
– Load Distribution: Studying gorilla posture helps inform architectural support systems, especially for cantilevered structures.
– Shock Absorption: The thick pads in gorilla hands and feet can inspire cushioning systems in buildings and vehicles.
Integrating these biomechanical principles into CAD projects enhances both functionality and durability.
Gorilla-Inspired Structural Design
Nature-inspired design, or biomimicry, is a growing trend in architecture and engineering. Gorilla anatomy, particularly the rib cage and limb bones, offers templates for:
– Truss Systems: Mimicking bone lattices for lightweight yet strong frameworks.
– Column and Beam Reinforcement: Drawing from the density and shape of gorilla bones for high-stress areas.
– Ergonomic Spaces: Using gorilla movement patterns to design accessible and comfortable environments.
CAD designers can incorporate these elements into DWG libraries, making them easily accessible for future projects.
Best Practices for Integrating Gorilla Models in CAD Workflows
When using gorilla models or anatomy references in CAD and DWG projects, consider the following:
– File Format Compatibility: Ensure models are available in DWG, DXF, and other widely-used formats.
– Level of Detail (LOD): Select models with appropriate detail for your application, balancing realism and performance.
– Parametric Design: Opt for parametric models that allow easy customization of size and pose.
– Metadata and Documentation: Include anatomical references and biomechanical data to enhance usability.
These practices streamline workflow and improve project outcomes for engineers and architects.
Conclusion
Gorillas are not just fascinating from a biological perspective—they offer practical inspiration for CAD designers, engineers, and architects. By leveraging accurate gorilla models and biomechanical principles, professionals can create stronger, more efficient, and innovative designs. Incorporating gorilla anatomy into DWG libraries supports a diverse range of applications, from structural engineering to ergonomic product development. For optimal results, always prioritize model accuracy, compatibility, and usability in your CAD projects.
Please log in or register to download this file.






Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.